-
病院紹介
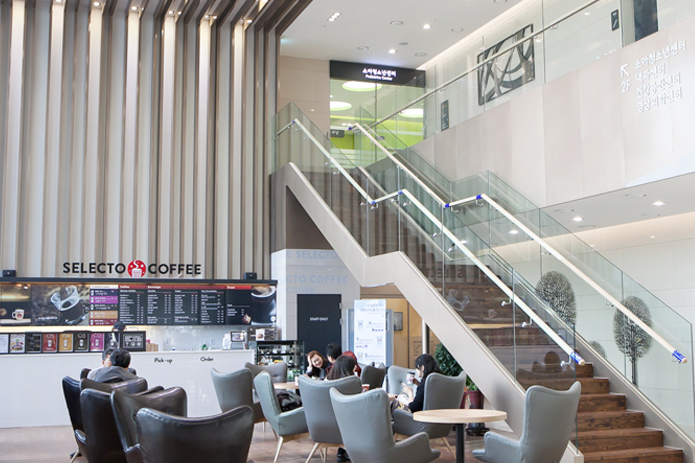
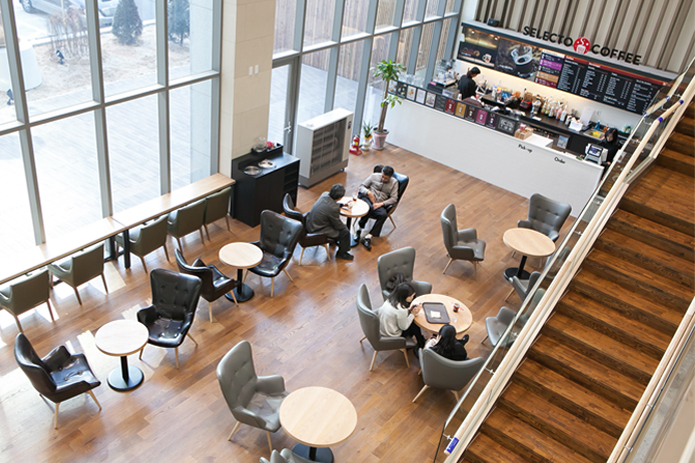
- フロアガイド
- 医療スタッフの
-
ビジョン
一定の研究と経験豊富な専門家

| ビジョン | コンフォートリラクゼーション親しみ

As a women' medical facility in Cheongna Int'l City, the Free Economic Zone of Korea, we serve a purpose as a general hospital with establishing Departments of Obstetrics/Gynecology, Women's Surgery, Internal Medicine, Pediatrics Adolescent, Anesthesiology/Pain Medicine, Dentistry, Dermatology, Postnatal Care Center, Medical Examination Center and Oriental Medical Clinic.
- High quality medical service from 20 excellent staff-doctors
- Obstetrics/Gynecology specialists are available 24hrs 365 days
- Separate clinics per gynecological diseases
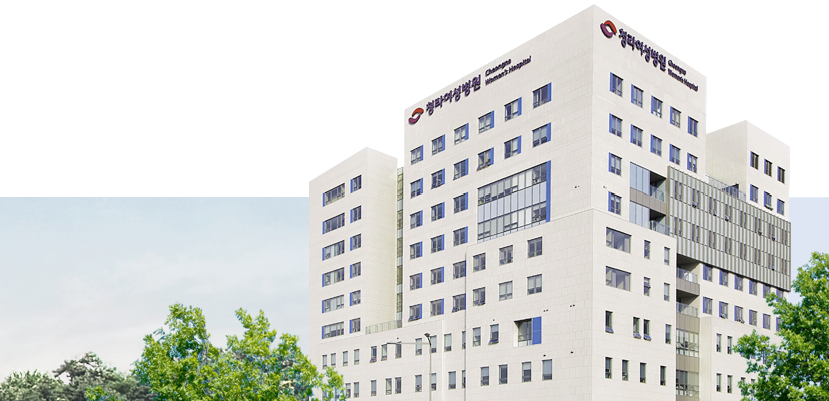
- A women's hospital in Incheon area with a grand scale
- Excellent medical facilities with luxurious but eco-friendly interior
- Birth with family, customized birth, special birth, naturalism birth are possible
- Mother and infant can stay in a same room to promote breast feeding
- Comprehensive nursing care from nurses by department
- Cooperation system among departments of Obstetrics/Gynecology, Pediatric Adolescent, Women's Surgery and Internal Medicine
- Operating Medical Examination Center
- Operating Love-and-Wish Center (Sterility)
- Medical service with Oriental Clinic and Dental Clinic.., and various amenities
- Comfortable facilities and high quality service from fertility to birth and even for postnatal care
- Gifts for birth and staying (?) postnatal care center
- Establishing cooperation system with 1st grade general hospital
-
ロケーション
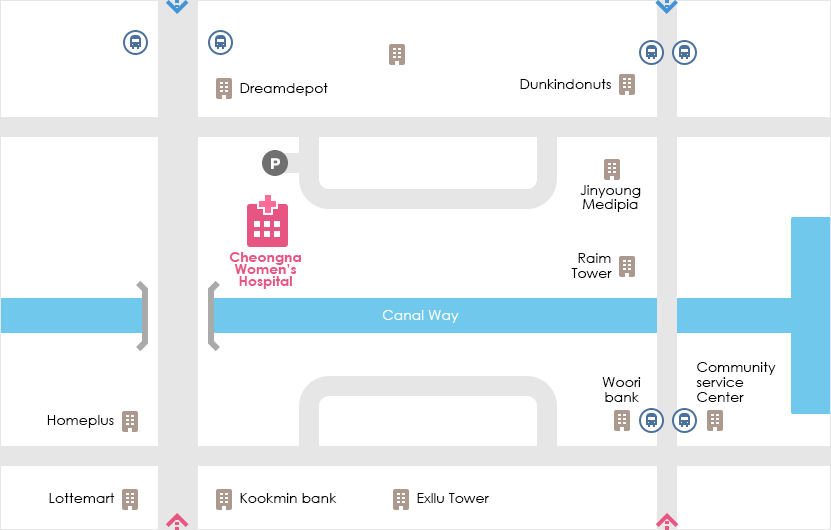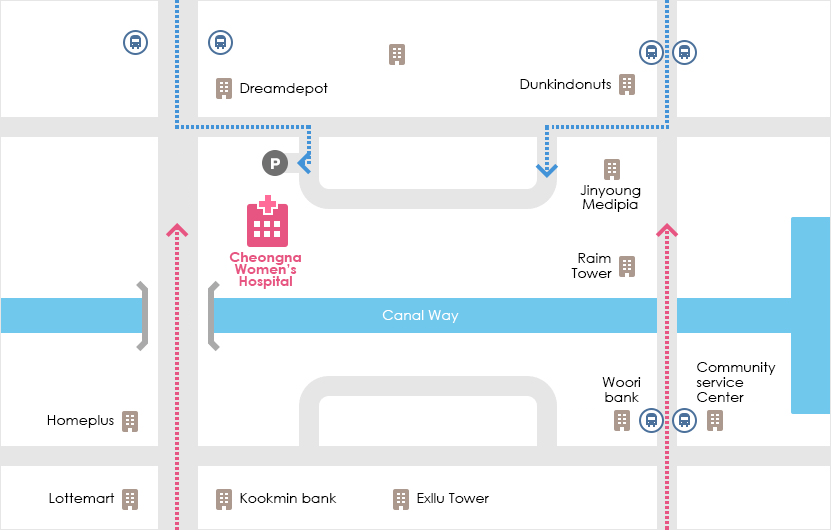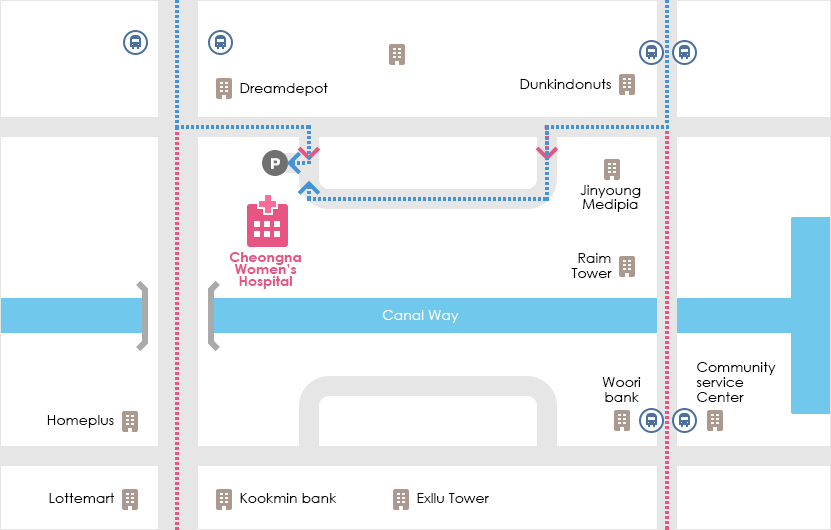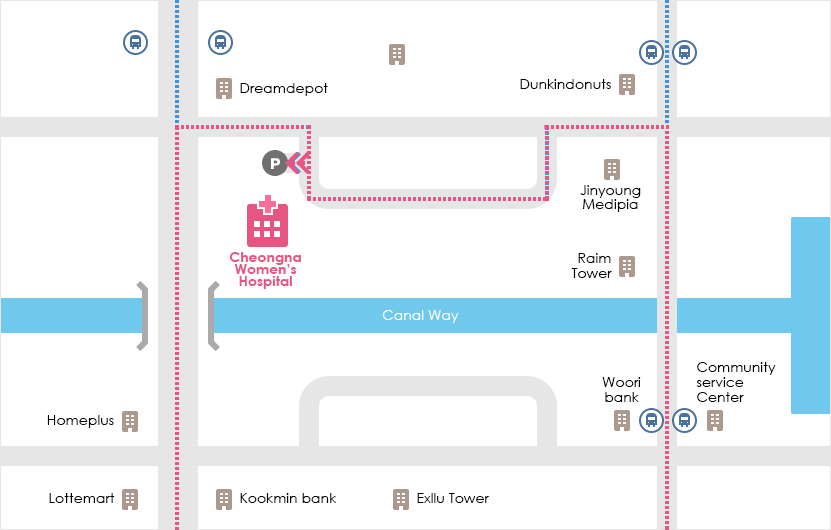
| 住所: 仁川広域市, 西欧ジュンボン通り602
駅 バス № Exllu Tower 42, 40, 41-1, 17-1, 595, 9300, M6118, 904-1 Poonglim Exllu Tower 221B, 223A, 306, 307 Jungbong Daero 7700 Community Service Center 2-1, 904 Gwangmyeong meiruz A 42, 42-1, 42-2, 46, 2-1, 72, 595, 904 空港からの道 - Take Airport Express at Gimpo/Incheon Int'l Airport → Get off at Geomam Station → Take Bus #591 - Get off at Homeplus bus stop
- Take Airport Express at Gimpo/Incheon Int'l Airport → Get off at Cheongna Int'l City Station → Take Bus #904 - Get off at Lynn Strauss bus stop
- Take Airport Express at Gimpo/Incheon Int'l Airport → Get off at Geomam Station → Take Bus #43-2 - Get off at Hoban Vertium Complex 14th bus stop
- Take Airport Express at Gimpo/Incheon Int'l Airport → Get off at Cheongna Int'l City Station → Take Bus #40 - Get off at Cheongna 2(il)-dong Resident Center bus stop
- Take Airport Express at Gimpo/Incheon Int'l Airport→ Get off at Cheongna Int'l City Station → Take Bus #46 - Get off at Gwangmyeong MAYLUZ bus stop
- 歓声
- 米軍の義務部
- 重点センター
-
外科センター
Laparoscopic surgery is a surgical technique, when a telescopic rod lens, connectable to a video camera for observing the abdominal cavity, is inserted through 5mm~10mm trocar
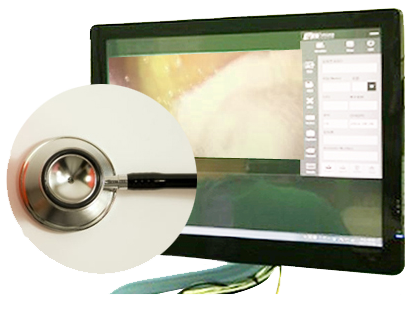
to confirm lesions on TV monitor after injecting carbon dioxide into the abdomen and operations are performed through other 2 small incisions on the lower abdomen. There is also a single-port laparoscopy, which requires only a single small incision of 1~1.5cm.
Laparascopic surgery also called pelviscopic surgery and even the laser laparascopic surgery, because sometimes it uses the laser cautery. And there is a hysteroscopic surgery, in which operations are performed in uterus by inserting camera and surgical instruments through vagina, when lesions ate located in uterus.
This laparascopic surgery is rapidly developing especially in the gynecology field and now it is introduced in the surgeries of gynecology such as treatments of ectopic pregnancy and endometriosis, ovarian tumor extirpation tubal replantation, myomectomy, hysterectomy and gynecological malignancy extirpation.
It is also used at the infertility clinic to investigate the causes of and to treat infertility.
CWH is performing all the mentioned surgeries with the state-of-the-art medical instruments of laparascopy and hysteroscopy.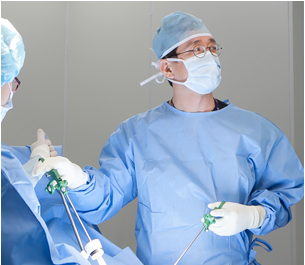
Advantages of Laparascopic Surgery
- Less pain. A lot less pain versus an open procedure.
- Less chance of side effects such as infection.
Reduced exposure of internal organs to possible contamination thereby reduced risk of acquiring infections. - Less hospital stay. Early discharge versus an open procedure.
- Short recovery time. Normally an immediate return to everyday living after discharge is possible.
- Less post-operative scarring. Smaller incision reduces size of scar resulting better aesthetic effect.
- More delicate operation is possible by securing expanded clear surgical view. Patients can be treated more delicately and accurately.
Disadvantages of Laparascopic Surgery
- Laparascopic surgery is clearly advantageous versus an open procedure.
- However, the surgery will be impossible by failure of securing clear view when adhesions of small intestine or large intestine are severe and serious. In this case, an open procedure is unavoidable.
It doesn't mean that laparascopic surgery is always impossible when there is an adhesion.
It depends on the degree of adhesion.

CWH can perform laparascopic and hysteroscopic surgeries, incliding
- Hysterectomy
- Myomectomy
- Myolisis
- Ovarian cystectomy or Oophorectomy
- eg, salpingectomy, salpingostomy
- Diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis
- Hysteroscopic polypectomy
- Tubal ligation
- Appendectomy
- 健康検診センター
- 産後調理員
- 治療のリクエスト
25~30% of adult females have uterine myoma with no symptoms thereby they are detected accidentaly during examination.
Benign muscle tumor in the uterine
Uterine myoma is a benign smooth muscle tumor of the uterus and most common woman' disease.
Women in age of 30~45 commonly develop it, however, it may be developed at any age.
It is known, that minimum 20% of women in their childbearing years have uterine myoma.
 | Causes & Symptoms of Uterine Myoma The exact cause of uterine myoma is unclear. Most common symptom is irregular menstruation, mostly hypermenorrhea of heavy period and atypical colporrhagia of vaginal bleeding when not during period. |
| Subserosal Myomas | They can be felt in abdomen area and make lower abdominal area felt heavy.
| |||
| Submucosal Myomas | Menorrhalgia, pain in lower abdomen | |||
| Intramural Myomas | Heavy period or vaginal bleeding when not during period |
 | Diagnosis by Ultrasonography The most common examination method to diagnosis uterine myomas:
|
Treatment
Most myomas are benign tumors, thereby they do not require treatment when there is no symptom and the sizes are small. However, they must be determined by specialist and those, who have symptoms such as frequent urination, feeling of residual urine, backache, heavy periods, anemia, menometrorrhagia, repeat abortion and infertility, need to get treatments.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy will be carried out for those women, who want to fertilite, to reduce the size of myomas or decrease bleeding. However, it must be used for short period, because longer use can cause multiple side effects, including amenorrhea. | Surgical Therapy
If the size of myoma is too large or there are multiple myomas, hyterectomy should be performed and it leads to infertility. Removing uterus can be recogmized as losing womanhood because uterus roles as the origin of life and gender identity for women. However, it doesn't effect much to the sexual life except there will be no vaginal discharge and the hormones are normally produced because menopause is not happened yet. |
Cervical Cancer Examination
 | Papanicolau Smear Papanicolau Smear (Pap Smear) contributes to early diagnosis of cervical cancer and to lowering frequency of infiltrative cervical cancer occurence. Examination is carried out by collecting secretion from cervix and vagina and dyeing in a special staining solution. If any abnormality is found from papanicolau smear, biopsy will be carried out for definite diagnosis. |
 | Advantages Cautions Examination period |
 | Telecervico Telecervico is an examination method using the principle of colposcope. |
 | Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Test It is carried out to determine whether the patient is infected with the HPV and whether the cancer will be developed. There are more than 80 kinds of HPV. About 30 kinds of them induce inflection on the cervix from sexual intercourse and around half of them are related to cervical cancer. There is no certain symptom and the inflection will disappear after suppressed existing. In extremely rare cases HPV develops to regular neoplasm in the epithelial cells. |
 | Biopsy If any abnormal lesions are found from papanicolau smear or colposcopic examination, the cervical cancer is confirmed from the result of biopsy. |